Modified by Simisola Fagbola, Econoday Financial Expert
The Economy
Monetary policy
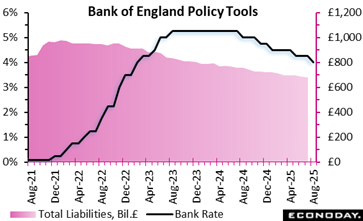
In a finely well balanced 5– 4 decision, the Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Board opted to reduce the Financial institution Rate to 4 percent, signifying cautious positive outlook in the disinflation journey. This step reflects an expanding idea that the most awful of inflation may lag, also as short-term pressures persist. Inflation has bordered up to 3 6 percent and is forecast to peak at 4 percent in September due to energy, food, and carried out costs. Nevertheless, under the surface area, pay development is easing and financial slack is arising, with weak GDP development and climbing joblessness recommending a softening work market.
Departments within the board emphasize varying top priorities. Some members pushed for a larger rate cut to sustain faltering demand and reduce economic downturn threats, while others stayed skeptical of sticky inflation assumptions, especially from families responding to high food and energy expenses. The vote records a turning point. The economic climate is no more overheating, but confidence in disinflation is not yet unanimous.
Markets had largely prepared for the cut, and with no pre-set course for plan, future actions will certainly rest on just how promptly inflationary stress moderate. This price cut, although moderate, represents a calculated shift from tight plan towards an extra growth-sensitive position.
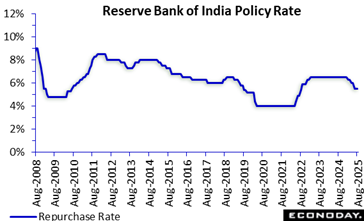
The Reserve Bank of India’s Monetary Plan Board has left its standard bought price on hold at 5 50 percent at its plan review held today, in line with the agreement forecast. Authorities cut this rate by 100 basis points over the previous three meetings after the price had actually been left on hold for two years.
Information launched considering that the RBI’s previous meeting in June have actually revealed headline CPI inflation moderating from 3 16 percent in April to 2 82 percent in May and 2 1 percent in June, back listed below the mid-point of the RBI’s target variety of two percent to 6 percent. This decrease was prepared for by officials and mainly reflects the influence of food prices. PMI survey data have shown strong conditions, though industrial manufacturing growth has actually moderated in recent months.
In the statement coming with today’s choice, RBI officials once again highlighted the recent decline in rising cost of living and suggested that good weather will likely further lower food rising cost of living stress. With the near-term rising cost of living overview currently “extra benign than prepared for earlier officials have lowered their inflation forecasts for this fiscal year from 3 7 percent to 3 1 percent. Authorities revealed worries concerning “headwinds emanating from long term geopolitical tensions” the impact of a “tough international setting” but shared confidence that residential demand will be supported by supportive monetary and financial plan and “jovial financial conditions.” They anticipate GDP growth of 6 5 percent this fiscal year.
Mirroring this analysis, authorities ended that policy setups need to be continued hold today as they “wait for more transmission of the front-loaded price cuts to the credit markets and the more comprehensive economic situation.” They also announced that they preserve the plan stance as “neutral” as they think about incoming information.
Demand
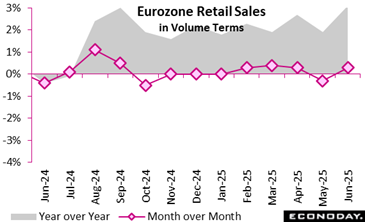
Retail activity in the euro area showed modest yet motivating development in June 2025, indicating a small rebound in consumer self-confidence. Retail trade quantity climbed by 0. 3 percent month-over-month, turning around the 0. 3 percent decline recorded in May. On a yearly basis, the retail index climbed up by a noteworthy 3 1 percent, reflecting healthier customer need compared to June 2024
Across classifications, all sections contributed favorably to this growth. Non-food products (excluding automotive fuel) blazed a trail with a 0. 6 percent monthly increase, recommending more powerful optional costs. Automotive fuel sales climbed by 0. 4 percent, and food, beverages, and cigarette edged up by 0. 2 percent, indicating consistent essentials-based intake.
The year-over-year data even more confirms this positive momentum as non-food products rose by 4 3 percent, while auto gas and food-related sales increased by 4.0 percent and 1 7 percent specifically. This broad-based growth mean easing inflationary stress and a very carefully improving customer outlook.
Overall, June’s data suggest of a retail sector regaining stability, fueled by a blend of necessity-driven and way of living purchases, supplying a welcome signal of resilience in the middle of broader financial uncertainty.
Manufacturing
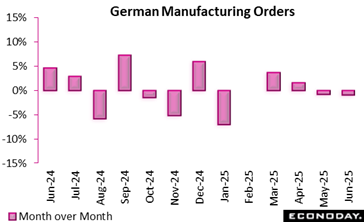
Brand-new orders in German manufacturing declined by 1.0 percent compared to May, driven greatly by a high decrease in massive transport equipment orders (minus 23 1 percent) and problems in the automotive (minus 7 6 percent) and steel item markets (minus 12 9 percent). Nevertheless, when omitting these massive orders, the image boosts slightly, with a modest 0. 5 percent increase month-over-month.
Year-over-year information reveals a plain comparison. While June saw just a 0. 6 percent boost from June 2024, May had actually reported a durable 6 3 percent growth over the previous year, partially due to a late-reported significant order that modified earlier numbers.
On an extra favorable note, intermediate items climbed by 6 1 percent, consumer goods by 0. 5 percent, and electric equipment soared (23 5 percent), assisting to support the decline. Domestic demand likewise showed durability, climbing up 2 2 percent, although international orders went down 3.0 percent, bore down by a 7 8 percent autumn from outside the euro area.
In spite of weaker orders, actual turn over in manufacturing grew by 0. 9 percent in June, recommending manufacturing procedures remained active. Generally, the data reflect underlying volatility and reliance on high-value transportation orders, with moderate domestic toughness stabilizing international need weaknesses.
International profession
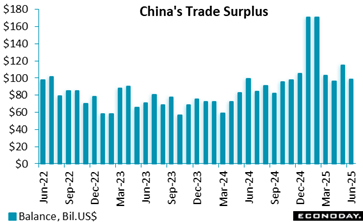
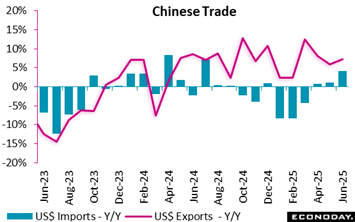
China’s merchandise profession surplus in United States dollar terms was $ 98 24 billion in July, tightening from $ 114 77 billion in June yet well above the level of $ 84 65 billion videotaped in July 2024 Exports climbed 7 2 percent on the year in July after enhancing 5 8 percent in June, while imports increased 4 1 percent, picking up from a previous rise of 1 1 percent.
Although the information revealed additionally weakness in Chinese exports to the USA, down 22 percent on the year, this was exceeded by stronger deliveries to various other significant trading companions. This may, partly, mirror the re-routing of exports ultimately destined for the United States as component of initiatives to prevent the influence of higher tariffs imposed on China by the Trump Management. Stronger exports to south-east Asia and Latin America, specifically, may be partly driven by this practice.
Service Studies
U.S. solutions market activity decreased in July, with expanding concern concerning employment and growing inflationary pressures.
The ISM Services acquiring supervisors index dipped to 50 1 in July from 50 8 videotaped in June and listed below the 51 5 expected in the Econoday study of forecasters.
“July’s PMI level remains to reflect sluggish growth, and study respondents showed that seasonal and weather condition aspects had negative impacts on service,” the record claimed. “The Employment Index’s continued tightening and faster expansion of the Consumer price indeces are worrisome growths.”
Business Task Index revealed development for July, however at a slower rate compared to June. Brand-new orders likewise broadened at a slower price, while employment shrank for the 4th time in the last 5 months.
Rates leapt compared to June and remain raised (the July price reading is the highest possible considering that October2022
United States Testimonial
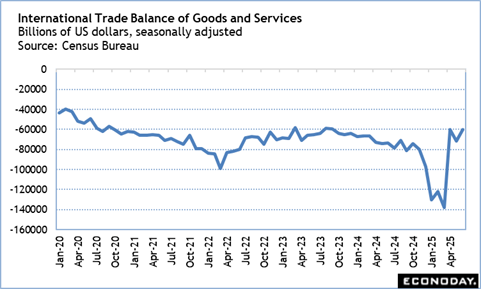
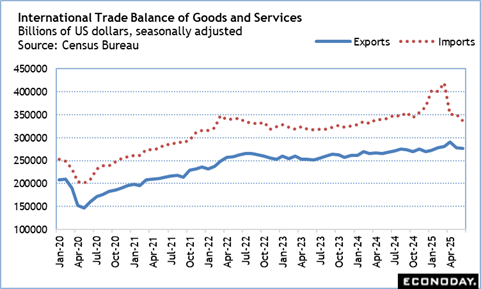
Trade Equilibrium Swings Back in 2 Q after Bump in Q 1; Trump Gets Opening at Fed Board
By Theresa Sheehan, Econoday Economist
The international trade equilibrium for June along with the profession equilibriums in April and May indicate a constricting in the profession deficit in the second quarter 2025 after a huge widening in the very first quarter. The first quarter saw companies stockpiling on tough goods ahead of expected huge walkings in tariffs that would certainly make imports more expensive– in some circumstances a lot more so. That has more or less ended, although still unclear toll policy may see ruptureds of activity to make use of periods when the imposition of tariffs are postponed.
It is a little tough to analyze out where changes the buck worth of imports and exports result from greater or lower rates, or adjustments in currency exchange rate, or to the quantity of goods and solutions.
What can be claimed is that the higher trend for exports appears to be regulating while the bump in demand for imports does not show up to have significantly deteriorated the hidden fad. However, trade contracts and tariff policy remain unpredictable and leave companies and consumer in a fog of uncertainty.
With the departure of Federal Book Governor Adriana Kugler, there is an opening on the Fed board for the presently unexpired term finishing January 31, 2026 Whoever is appointed to change Kugler will certainly submit the last months of that term. It would be a regular technique to authorize the candidate for the subsequent 14 -year term finishing January 31, 2040 Nevertheless, that have to be specific in the formal election sent out to the Senate. Head of state Trump has claimed he will nominate the present chair of the Council of Economic Advisors Stephen Miran to load the remaining six months.
There is little reason to think that the vote in the complete Senate will not authorize this election once the confirmation process is full. The enhancement of a Trump partisan to the board of guvs is a growth that will certainly include in concerns regarding the Fed’s freedom. This is especially the situation after Guv Christopher Waller– proclaimed as a possible successor to Chair Jerome Powell– and Vice Chair for Guidance Michelle Bowman dissented in the vote of the July 29 – 30 FOMC meeting. Waller and Bowman are both Trump appointees. Both agree that the rate rises from tariffs will be temporary and feed rising cost of living over the longer term. Miran would certainly share their views.